Cars running in towns in the near future will be almost replaced by electric vehicles. Exactly electric vehicles are now in progress and are continuing to evolve. A major problem is how to cope with the heat buildup caused by the increase due to components such as semiconductor elements, LED lamps and high-output batteries, as well as by the densification of components resulting from the miniaturization of vehicle bodies. Heat dissipation materials that can control such heat are becoming key materials not only in the automotive industry but also in various fields.
Here, we will introduce the characteristics, types, and applications of heat dissipation material dispersions.
What is heat dissipation material dispersion?
The following three types of heat transfer are available:
1) Heat conduction: A phenomenon in which heat is transferred from a high-temperature part in a substance to a low-heat part by vibrations of molecules or transfer of free electrons.
2) Heat transfer (convection): A phenomenon in which a flowing substance such as gas or liquid transfers heat through convection.
3) Heat radiation: The phenomenon of radiating heat energy from an object in the form of an electromagnetic wave.
The above three heat transfer methods can be considered as the heat dissipation elements from the heat source, the substrate, and the heat sink. Every substance is transferred from a high to a low heat energy site through a combination of three heat transfers. However, there are differences in the way heat is transferred depending on the substance and environment.
Coating a product with a heat source inside with a material with a high thermal conductivity enhances thermal conductivity, transfers heat to the product surface, and efficiently transfers heat through heat transfer and heat radiation, thereby enhancing the heat dissipation function.
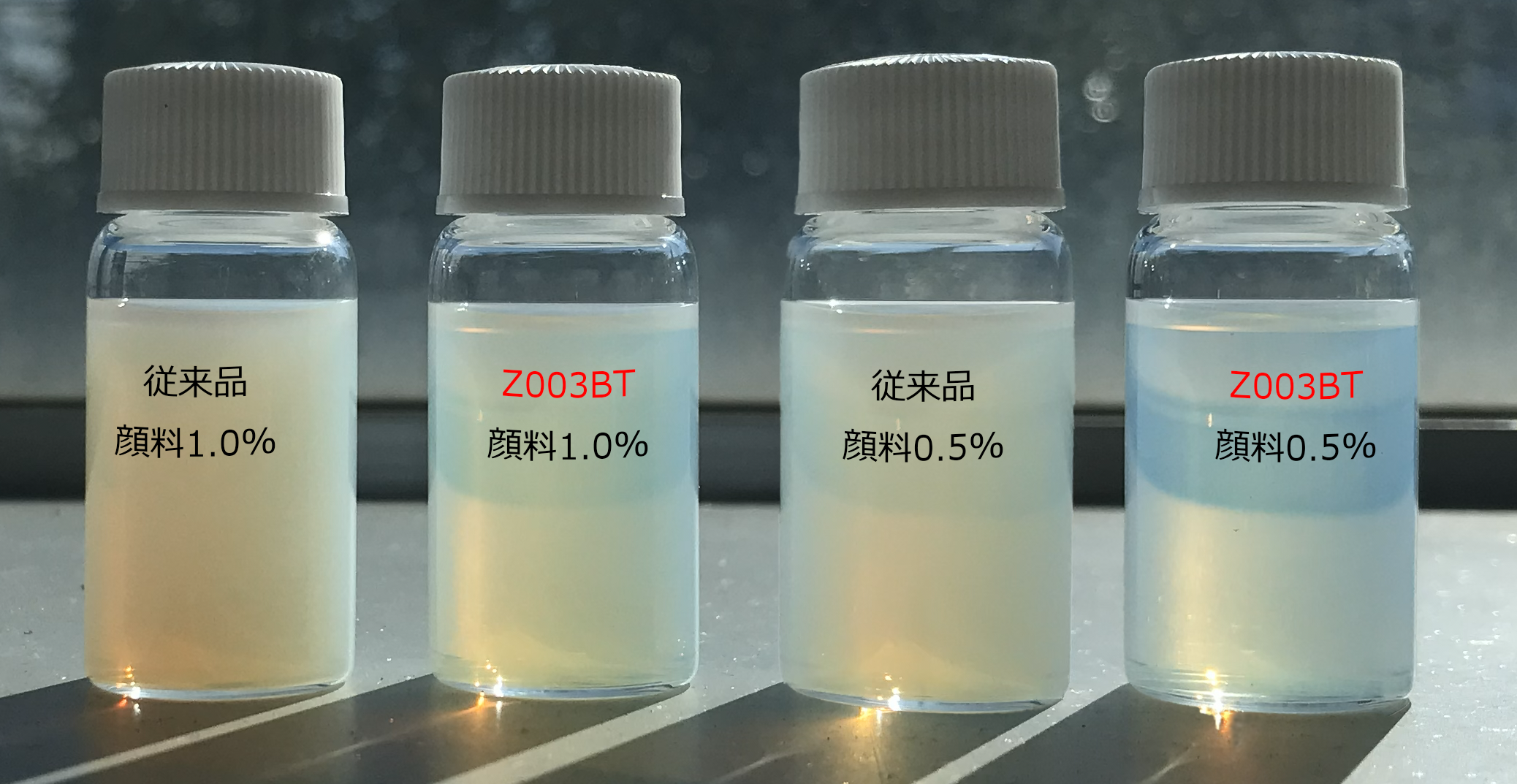
The type and concentration of heat dissipation material (in the coating film) determine the amount of heat transfer. Generally, the higher the concentration of heat dissipation material (the denser the particles) the higher the heat radiation.
TOKUSHIKI selects highly thermally conductive materials and disperses them in various solvents to make the heat-dissipating material more dense. We believe that it is possible to impart heat-dissipating functions to various paints, inks, and other materials.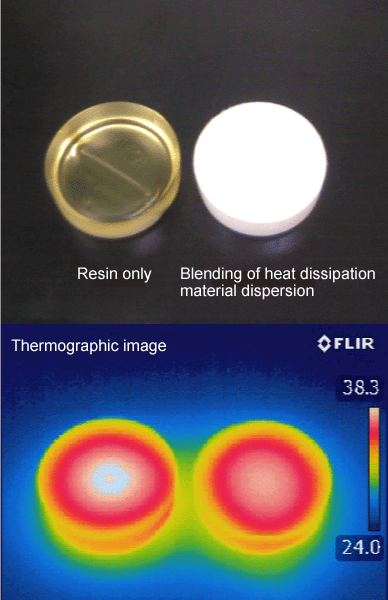
Application and lineup of heat dissipation material dispersion
Applications: Heat-dissipating paint, heat-dissipating sheet, heat-dissipating grease, heat-dissipating substrate, heat sink, etc.
Lineup:
| Product name | Description |
|---|---|
| 9058ZO | Organic solvent-based (non-aqueous) zinc oxide dispersions |
| 9059ZO | Aqueous zinc oxide dispersion |
| 9066AN | Organic solvent-based (non-aqueous) aluminum nitride dispersions |
| 9082MO | Organic solvent-based (non-aqueous) magnesium oxide dispersions |
| 9206DO | Organic solvent-based (non-aqueous) composite oxide dispersions (highly dispersed) |
| 9207DO | Aqueous composite oxide dispersion (high dispersion) |
| 9208DO | Organic solvent-based (non-aqueous) composite oxide dispersion (medium dispersion) |
| 9209DO | Aqueous composite oxide dispersion (medium dispersion) |
| 9210DO | Organic solvent-based (non-aqueous) composite oxide dispersions (low dispersions) |
| 9211DO | Aqueous composite oxide dispersion (low dispersion) |
| 9212BN | Aqueous boron nitride dispersions |
| 9215AO | Organic solvent-based (non-aqueous) aluminum hydroxide dispersions |
| 9216AO | Aqueous aluminum hydroxide dispersion |
| 9217MC | Organic solvent-based (non-aqueous) magnesium carbonate |
| 9218MC | Aqueous magnesium carbonate |
*Composite oxides are classified according to particle size and solvent type. It can be made close filling by blending. Can be blended to suit your application.
*There are differences in thermal conductivity, ease of processing (dispersion), solvent resistance, water resistance, and cost depending on the heat dissipating material, and it is necessary to use them according to their characteristics.
Inorganic filler dispersion(under development)
Summary
- TOKUSHIKI is developing dispersions of materials with thermal conductivity properties.
- It is expected that the heat dissipation function will be imparted by doping the dispersion liquid in which the heat dissipation material is dispersed in a solvent into various paints, inks, and the like.
- Each of the heat-dissipating materials in which TOKUSHIKI is dispersed has its own characteristics. It can be used depending on the application and can be blended.





